Understanding the Structure and Components of Medical Syringes
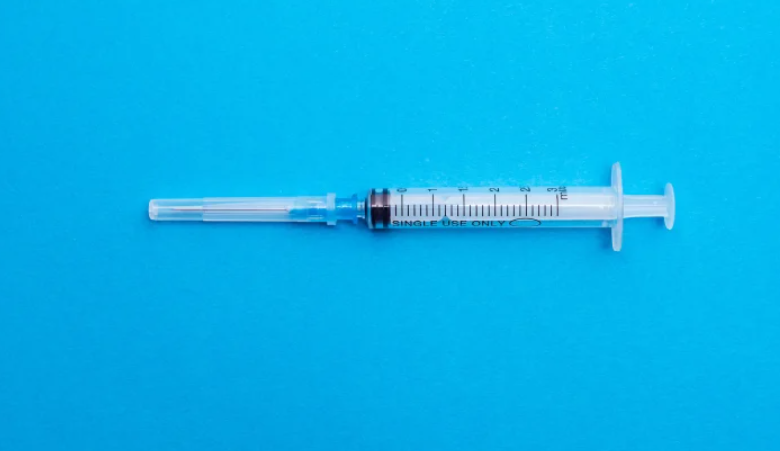
Introduction to Medical Syringes
Medical syringes are critical instruments in healthcare, widely used for administering medications, vaccines, and other therapeutic fluids. The efficiency and safety of these devices depend on their design and the quality of their components. Understanding the parts of syringe is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure accurate dosage, minimize patient discomfort, and prevent errors during administration.
Main Components of a Syringe
A syringe typically consists of several key parts, each designed to perform specific functions. Familiarity with these components ensures proper usage and enhances patient safety.
Barrel
The barrel is the cylindrical container that holds the fluid. Transparent barrels usually have measurement markings, which are crucial for accurate dosing. In pediatric or laboratory settings, precise measurements are vital to prevent over- or under-dosing.
Plunger
The plunger is a movable part inside the barrel that creates suction to draw fluid and pushes it out during administration. The plunger must move smoothly to allow controlled injection, ensuring patient comfort and accurate medication delivery.
Needle
The needle attaches to the syringe and acts as the passage through which medication enters the body. Needle selection is based on injection type, fluid parts of syringe viscosity, and patient age or condition. Choosing the correct needle reduces pain and ensures proper delivery.
Tip Connection
Syringes can have either Luer lock or slip tip connections. Luer lock tips secure the needle to prevent detachment, while slip tips allow quick attachment and removal. The choice depends on procedure requirements and safety considerations.
See also: Enhancing Healthcare Management with Patient Statement Printing and Mailing Services
Detailed Analysis of Syringe Parts
Understanding the parts of syringe allows for better handling, maintenance, and patient care.
Barrel Design Variations
Barrels can vary in size and design depending on their application. Smaller barrels are ideal for precision dosing, while larger barrels accommodate higher-volume injections. Ergonomic barrels are designed for a comfortable grip, aiding healthcare professionals during repetitive procedures.
Plunger Types
Plungers differ in materials and design. Some feature rubber seals to create airtight pressure, while others have smooth surfaces for specialized uses such as insulin injections or laboratory experiments. Proper plunger function ensures accurate dosing and reduces medication waste.
Needle Variations
Needle types vary by length, gauge, and bevel. A higher gauge means a thinner needle, which is less painful and suitable for subcutaneous injections. Lower gauge needles are thicker and often used for intramuscular injections or thicker fluids. Selecting the correct needle is essential for safe and effective administration.
Safety Features
Modern syringes often incorporate safety elements, including retractable needles, safety caps, or prefilled designs to prevent contamination. Knowledge of these parts ensures healthcare workers select the right syringe for each patient while minimizing risks of needlestick injuries.
Applications in Healthcare
Understanding the parts of syringe is essential across various medical scenarios.
Medication Administration
Proper handling and knowledge of syringe components ensure accurate delivery of medications. The combination of barrel, plunger, and needle affects dosage precision and ease of use.
Vaccinations
Vaccines require precise injection into specific tissues. Choosing the correct needle size and syringe volume ensures efficacy and reduces discomfort, especially in pediatric patients.
Laboratory Use
In research and laboratory settings, syringes are used for precise fluid handling and sample collection. Knowledge of syringe parts ensures sample integrity and accurate experimental outcomes.
Pediatric and Geriatric Care
Children and elderly patients may need special syringes with smaller barrels and fine needles. Understanding parts of syringe allows healthcare providers to minimize discomfort and anxiety during injections.
Maintenance and Safety Practices
Even though syringes are typically disposable, understanding their parts is vital for safe use:
- Inspect syringes before use for damage in the barrel, plunger, or needle
- Always use sterile syringes to prevent contamination
- Dispose of used syringes in designated sharps containers
- Avoid recapping needles to reduce injury risk
Innovations in Syringe Design
Advancements in medical technology have improved syringe designs:
- Prefilled syringes: Reduce preparation time and contamination
- Safety-engineered syringes: Prevent accidental needlestick injuries
- Ergonomic barrels and plungers: Enhance comfort and precision
Healthcare professionals who understand the parts of syringe can take advantage of these innovations for improved patient outcomes.
Enhancing Patient Comfort
Proper knowledge of syringe parts not only ensures accurate dosing but also reduces patient discomfort. Thinner needles, smooth plunger action, and ergonomic barrel designs all contribute to a less painful injection experience. Patients who feel comfortable are more likely to cooperate during procedures, especially children or anxious individuals.
Environmental Considerations
Syringe disposal is a crucial aspect of medical practice. Used syringes must be placed in approved sharps containers to protect healthcare workers and the environment. Some syringe components are recyclable, but healthcare providers must understand which parts can be safely disposed of without compromising safety.
Training and Education
Healthcare professionals must be trained in the use and handling of syringes. Knowledge of parts of syringe supports safe administration, precise dosing, and effective patient care. Ongoing education ensures that medical personnel remain up-to-date with advances in syringe technology.
Conclusion
Syringes are indispensable tools in healthcare, and understanding the parts of syringe is fundamental to safe and effective medication administration. Each component, from the barrel to the needle, contributes to accuracy, patient comfort, and safety. By mastering the structure and function of syringes, healthcare professionals can enhance patient outcomes, prevent errors, and utilize modern innovations efficiently. Knowledge of syringe parts is an essential skill for anyone involved in clinical, laboratory, or pediatric care.



