Where Should You Deploy a PTZ Camera for Maximum Coverage?
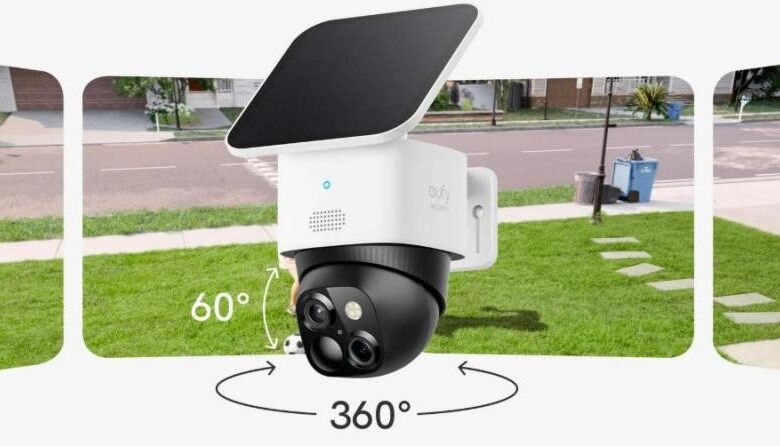

PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras are revolutionizing the way we think about surveillance. These cameras provide the flexibility and control needed for comprehensive monitoring. By strategically positioning PTZ cameras, users can ensure full visibility and make monitoring more efficient. Whether employed in residential settings, businesses, or public areas, understanding optimal placement is vital. The deployment of PTZ cameras goes beyond mere installation; it involves recognizing how best to capitalize on their capabilities. Each environment demands careful consideration of installation practices to harness its full potential. This guide will explore best practices for achieving maximum coverage with PTZ cameras, ensuring security needs are thoroughly met.
Understanding PTZ Camera Coverage
PTZ cameras offer dynamic coverage, making them suitable for both wide-area and detailed monitoring. These cameras can pan horizontally, tilt vertically, and zoom into specific areas, providing a 360-degree field of view when strategically placed. This capability allows users to cover large spaces without multiple stationary cameras. By understanding their mechanics, one can effectively maximize their functionality. For instance, in a business setting, a single PTZ can oversee a vast floor space, while at home, it might be used to monitor a backyard or driveway. Recognizing this versatility is key to efficient camera deployment. Mastering PTZ coverage ensures users make informed decisions on placement, securing comprehensive surveillance and monitoring.
Optimizing Camera Placement for Maximum Coverage
Ideal Mounting Heights and Angles
When installing a PTZ camera, selecting the right height and angle is crucial. Placing cameras too high might limit their zoom functionality, whereas installing them too low can restrict their panoramic view. Generally, installing PTZ cameras at a height of 8 to 10 feet is recommended. This height allows for optimal pan and tilt movement, covering wide areas effectively. When considering angles, aim for positions that provide clear sightlines without obstructions. For example, positioning a camera at the corner of a building can maximize coverage by minimizing blind spots. Careful calibration ensures the camera covers intended areas without unnecessary overlaps or missed spots.
Avoiding Blind Spots and Overlaps
Blind spots can undermine the effectiveness of PTZ cameras, so avoiding them is paramount. Start by conducting a thorough assessment of the area to be monitored. Identify potential obstructions like trees, walls, and furniture that could block the camera’s view. Adjust camera angles and positions until blind spots are eliminated. Using digital tools or software during planning can provide a virtual layout to help forecast any potential issues. Further, while overlaps might seem beneficial, they can lead to inefficiencies and unnecessary coverage redundancy. Balance is key; aim for strategic placement that maintains visibility without wasted resources.
Using Multiple PTZ Cameras for Layered Security
To achieve layered security, integrating multiple PTZ cameras is a sound strategy. This approach allows seamless coverage by having cameras focus on different zones. In an office complex, one camera might monitor entrance points while another oversees parking areas. Integrating them with a centralized system ensures holistic management and quick response times. Each camera complements the others, creating a network that can adapt to evolving security needs. This method not only enhances coverage but also adds redundancy, ensuring that if one camera is compromised, others can continue monitoring without interruption.
Best Practices for Outdoor vs. Indoor PTZ Installation
Outdoor Setup: Weather Resistance and Lighting Conditions
Outdoor PTZ installations face unique challenges, primarily weather resistance and lighting. It is essential to choose cameras built to withstand the elements, featuring waterproof and dust-resistant designs. Additionally, consider the camera’s ability to adapt to changing lighting conditions. Incorporating infrared or night vision capabilities can maintain effectiveness even in low-light situations. Position cameras where they are not directly exposed to harsh sunlight, which can impede visibility and cause premature wear. With thoughtful placement and technology, outdoor PTZ cameras can deliver reliable, round-the-clock surveillance.
Indoor Setup: Discreet Mounting and Power Access
Indoor PTZ installations prioritize discretion and power access. Select locations where cameras can be easily concealed without compromising their functionality. Ceiling corners often provide ideal vantage points, offering comprehensive views while remaining unobtrusive. Ensure there’s access to power sources, considering wireless options if typical setups pose challenges. Prioritize locations that require minimal intrusion for maintenance or adjustments. Discreet, strategic indoor placement not only meets security goals but also aligns with aesthetic considerations, balancing monitoring needs with environmental design.
Conclusion
Deploying PTZ cameras effectively enhances security capabilities through strategic placement and installation. Understanding the mechanics of PTZ cameras aids in maximizing their coverage, ensuring comprehensive visibility, and efficient monitoring. Consideration of mounting heights, angles, and environmental specifics such as weather and lighting conditions is essential. Integrating multiple cameras for layered security and recognizing the differences between indoor and outdoor deployments further enhances efficacy. By following these practices, you can optimize the operation of PTZ cameras, achieving robust security measures tailored to both personal and professional environments.